
New research reveals AMOC is not as close to a catastrophic decline or major tipping point as previously thought
By
New research by a team of researchers from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) has revealed the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is more stable than expected, overturning previous assumptions that the vast network of ocean currents has already declined.
Enjoying this article? Check out our related reads:
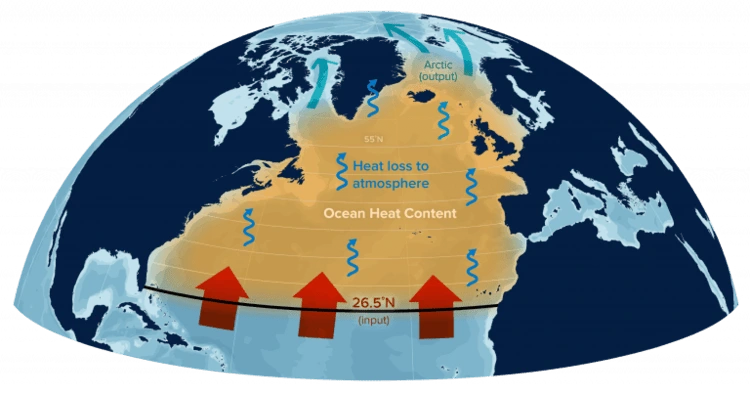
The AMOC plays a major role in moving water across the world’s oceans through a series of interconnected currents, forming a ‘global conveyor belt’ that shifts sediment, organisms and heat. It’s also involved in the regulation of Earth’s climate and weather.
Previously, scientists have raised concerns that the effects of a changing climate, combined with newly released freshwater from melting ice sheets, could either disrupt or entirely collapse the AMOC. Such a scenario would have major impacts from rising sea levels, more extreme winters – with temperatures plummeting an average of 10-15C across Europe – and ecological shifts reducing rainfall and halting crop harvests.
But the latest research, published in Nature Communications, suggests the AMOC is not as close to this tipping point as once thought.
Researchers used 24 different climate-earth models to ascertain the status of the AMOC, forgoing sea surface temperature data – as it did not accurately reconstruct the current network – for another measure: air-sea heat fluxes (when heat moves from the ocean to the atmosphere). Air-sea heat fluxes are closely linked to the AMOC: when the AMOC is stronger, more heat is released into the atmosphere.
‘Our paper says that the Atlantic overturning has not declined yet,’ said adjunct scientist in Physical Oceanography at WHOI, assistant professor at the University of Georgia and author of the study Nicholas P. Foukal, ‘That doesn’t say anything about its future, but it doesn’t appear the anticipated changes have occurred yet.’
The new study contradicts a paper from 2018, which reported the AMOC has undergone a decline in the last 70 years. But the 2018 paper used sea surface temperature measurements to understand the AMOC’s shifts, data that author of the new study, affiliated scientist at WHOI and senior scientist at the University of Bern Jens Terhaar explains ‘doesn’t work as well as initially thought.’
‘It’s almost unanimous at this point that the Atlantic overturning will slow in the future, but whether or not it will collapse is still up for debate,’ said Foukal. ‘This work indicates that there is still time to act before we reach this potential tipping point.’




